The Fourier series of a real function $f$ defined on the interval $(-p,p)$ is given by
Consider the function defined by $f(x)=x+\pi$ for $-\pi < x < \pi $ and $f(x)=f(x+2\pi)$ for $-\infty < x < \infty$. Its Fourier series expansion is \[ f(x)=\pi+2\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}\frac{\left(-1\right)^{n+1}}{n}\sin (n\,x). \]
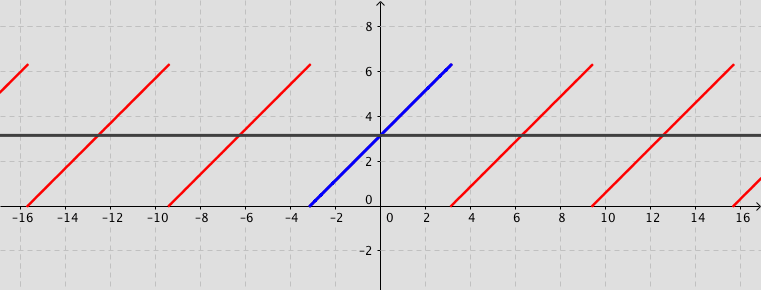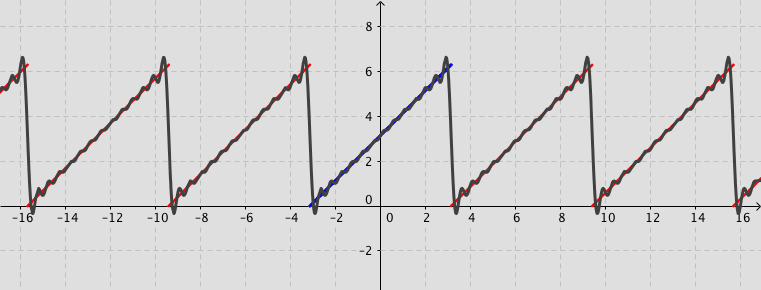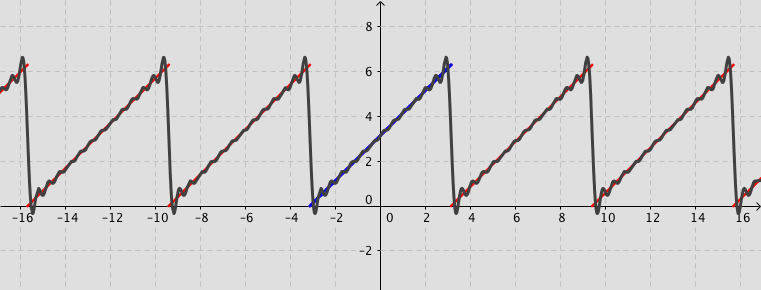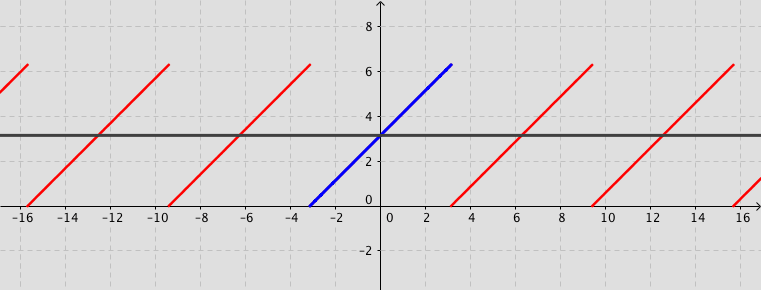
The following simulation shows the partial sum of the Fourier series (up to 20 terms) for a given function $f(x)$ (defined by user).
Remark: You can observe how the partial sum converges to the given function by increasing the number of terms. Activate the box Fourier series. Use the tools Zoom In or Out, if needed.
Other examples to try:
The following simulation shows the partial sum of the Fourier series (up to 20 terms) for a given function $f(x)$ (defined by user). However, the partial sum is NOT CORRECT, since the terms $a_0$, $a_1$ and $b_1$ are all zero by default in the simulation.
Calculate the Fourier series of the function and then type the CORRECT values of the coefficients $a_0$, $a_1$ and $b_1$ rounded to two decimal places.
For example, the coefficients for the default function $|x|+x$ are $a_0=1, a_1=-0.41$ and $b_1=0.64.$ Type these values in the corresponding boxes.
The following file contains activities and problems associated with the simulations.